C lower frequency at the anode end. The lowest energies are always approximately 15 to 20 keV and the highest energies are always equal to the kVp set on the control panel.
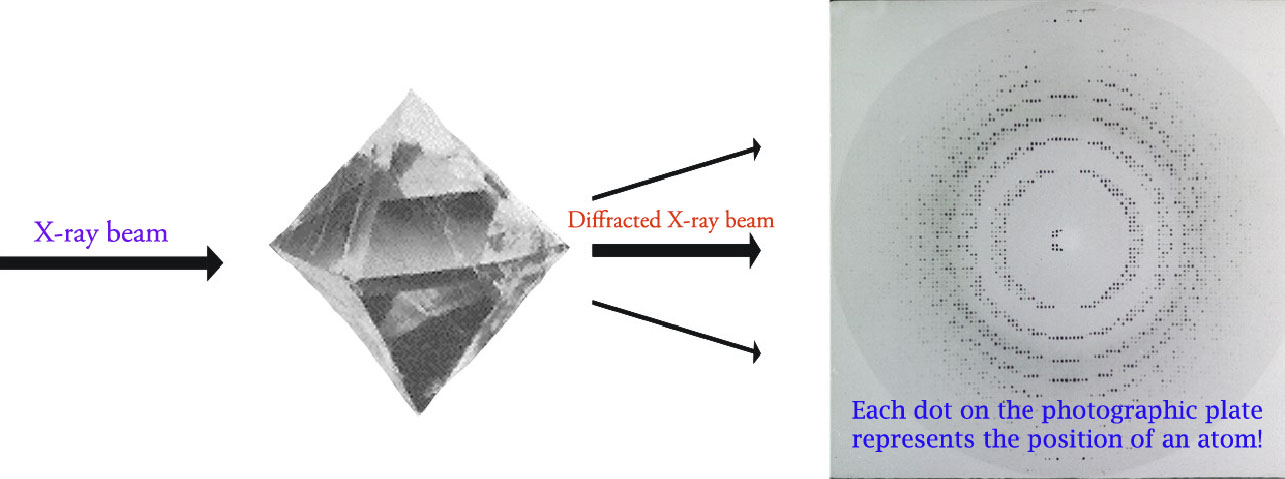
Diffraction Basics Chemical Instrumentation Facility Iowa State University
Cross section of xray beam is called the radiation field.

. When an x-ray beam is directed at a metallic crystal the beam hits the atoms and produces two types of x-rays white x-rays and characteristic x-rays. When a free electron fills the shell a x-ray photon with energy characteristic of the target material is emitted. X-ray mirrors rely on the same effect referred to in our discussion of X-ray reflectivity namely that a beam which strikes a flat surface at a very low angle can be strongly reflected.
X-rays travel in straight lines. Specialized X-ray sources detectors and analysis techniques have been developed to address a range of questions from the study of. For example an 80-kVp x.
These two focal projections are necessarily about 90 apart in the plane normal to the. Increase fluid and fiber intake for several days. X-Ray beams that are parallel with the narrow projection of the filament have an approximate focal shape of a square which is usually labeled as a spot.
A lower intensity at the anode end. The electron cloud within the x-ray tube is the product of a process called. Imaginary perpendicular ray at its center is called central ray.
These x-ray spectra represent local L and partial P electron density of states DOS because of the. Even though much of the literature focuses on chest computed tomography CT and X-ray imaging and their findings other imaging modalities have also been useful in the assessment of COVID-19 patients. B more energy at the cathode end.
Elastic interactions and inelastic interactions. Each of the following changes will serve to decrease the radiographic density by one-half except change to. From the focal spot the xray diverge into space forming the cone-shaped primary xray beam.
When electrons have sufficient energy to dislodge inner shell electrons of the target material characteristic X-ray spectra are produced. The defining characteristics of X-raystheir ability to penetrate optically opaque materials their wavelengths of atomic dimension the high energy of individual X-ray photonslead to a wide range of industrial medical and scientific applications. The cross section of the xray beam at the point where it is utilized is called the radiation field.
Which of the following isare characteristics of the x-ray tube. The cathode assembly receives both low and high voltages. Coherent X-ray beam metrology enabled by a.
The kV mA and exposure time are the three major selectable parameters on the x-ray generator control panel that determine the x-ray beam characteristics. The following methods are used to relax the constrains in order to achieve diffraction peaks 1. White x-rays include a wide range of wavelengths and are not of interest in this experiment.
The useful beam emerges from the port window. Body parts further away from the detector are magnified compared with those that are closer. Bond-lengths and angles are directly related to the atomic positions.
Occasionally magnification can be helpful in localising abnormalities. As a result of characteristic and bremsstrahlung radiation generation a spectrum of X-ray energy is produced within the X-ray beam. The intensity patterns produced were obtained in situ with a.
If a quantity of radiation is delivered to a body over a long period of time the effect. The crystal structure of a mineral is a characteristic property that is the basis for understanding many of. This spectrum can be manipulated by changing the X-ray tube current or voltage settings or by adding filters to select out low energy X.
These spectra consist of several components the most common being K α and K β. Characteristics of the primary x-ray beam include. Lung ultrasonography is an emerging technique with a high sensitivity and thus useful in the initial evaluation of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Characteristic x-rays are caused by the. Identification of phases is achieved by comparing the X-ray diffraction pattern. The target material should have a high atomic number and a high melting point.
Invisible weightless travel in a straight line. 1 while the x-ray absorption spectra reflect the unoccupied molecular orbitals MO. Which of the following are characteristics of x-ray beams.
X-ray mirrors are typically made of a metal such. The degree of collimation and spectral selection depend on the perfection of the crystal and also the characteristics of the incoming beam. X-Ray beams that are parallel with wide projection of the filament have a focal shape of a line.
The x-ray emission spectra reflect the occupied electronic structure as shown in Fig. Which of the following is are characteristics of the x-ray tube. The effects of radiation on biologic material depend on several factors.
Single-shot and acquired with a LiF crystal imaging detector. Used to describe the energy or penetrating ability of the x-ray beam. These interactions can be divided into two major categories.
Common targets used in x-ray tubes include Cu and Mo which emit 8 keV and 14 keV x-rays with corresponding wavelengths of 154 Å and 08 Å respectively. Often the product of the tube current and exposure time is considered as one entity the mAs milliampere-second. Three characteristics of the x-ray beam.
The specific wavelengths are. X-ray diffraction XRD is a versatile non-destructive analytical method to analyze material properties like phase composition structure texture and many more of powder samples solid samples or even liquid samples. The x-ray beam is polyenergetic many energies and consists of a wide range of energies known as the x-ray emission spectrum.
X-rays travel in straight lines and a beam of X-rays diverges from its source. Combination of the number of x-ray photons quantity and the energy of each photon quality. X-ray energy is measured in kiloelectron-volts keV 1000 electron volts.
Single-crystal X-ray diffraction is most commonly used for precise determination of a unit cell including cell dimensions and positions of atoms within the lattice. Refers to the number of x-rays produced in the dental x-ray beam. K α 1 has a slightly shorter wavelength and twice the intensity as K α 2.
Amount of radiation reaching the film distance from x-ray tube to the patient. Laue method Fix the orientation of the single crystal. The target material should have a high atomic number and a high melting point.
Search for Bragg peaks by using not a monochromatic x-ray beam but one containing wavelength for up to λ1. X-ray emission spectra of solids and molecules are methods of measuring electronic structure of matter 15. Which of the following affects the density of a radiograph.
In addition to elastic and inelastic interactions other interactions that are produced between an electron beam and a specimen include characteristic X-rays Auger electrons and cathodoluminescence. K α consists in part of K α 1 and K α 2.

X Ray Crystallography An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Digital Radiography Image Artifacts Radiology Suny Upstate Medical University

Chest X Ray 4 Years Later Showing Reticulonodular Pattern With Download Scientific Diagram
0 Comments